-
-

Aviation
Aircraft frame beams, landing gears, fasteners, and other rotating components like engine fans and compressor rotor blades.
-

Aerospace
Rocket engines, artificial satellite shells, fuel tanks, pressure vessels, manned spacecraft.
-

Shipbuilding
Submarine pressure hull, propeller, water jet propulsion system, seawater heat exchange system, ship pumps, valves, and pipelines.
Aviation, Aerospace and Shipbuilding
Titanium and zirconium alloys can be applied to key moving parts of space machines. They have a lower density and can make a huge contribution to the weight reduction of satellites and other spacecraft. They also have a lower coefficient of thermal expansion, are resistant to low temperatures in space, adapt to alternating temperature fields, and have good adaptability to space environments. This makes titanium and zirconium alloys more reliable and stable during service. Under extreme low-temperature conditions of minus 100℃, its strength is significantly enhanced.
Major titanium users in the aerospace sector are concentrated in the West. The United States, in particular, applies 60% of its titanium materials in this field. Asian countries like Japan and China invest around 10% of their titanium in this sector. It is expected that the average demand for titanium materials in commercial aircraft will reach 40 tons per aircraft within 20 years. Based on this calculation, the global demand for titanium materials in commercial aviation will increase by about 1.2 million tons in the next 20 years, with a compound annual growth rate of about 17%. The average annual demand for titanium materials will increase by 60,000 tons. We will see rapid growth in the field of titanium materials used for civil aviation.
-
-
-

Exterior walls and decorations of buildings
-

Railings and pipelines of buildings
Construction Industry
Traditional metal building materials are mainly copper, iron, aluminum, and stainless steel. With the progress of society, people have increasingly high requirements for buildings and tend to use more advanced building materials.
Titanium and its alloys have a series of excellent characteristics such as low density, high strength, good corrosion resistance, low thermal expansion coefficient, no environmental pollution, and long service life, which can fully meet the many performance requirements of building materials and are highly favored by modern architects.
-
-
-

Harbor Architecture
Offshore oil and gas development, seawater desalination equipment, coastal power plants
-

Ship
Hull structural components, propellers and propeller shafts in power-driven units, heat exchangers, coolers, hull sonar deflectors
-

Pipeline for Seawater Desalination
Pumps, valves, and fittings for offshore oil drilling
Marine Engineering
Titanium is a material with excellent physical properties and stable chemical properties. Titanium and its alloys have high strength, low specific gravity, resistance to seawater corrosion and marine atmosphere corrosion, and can well meet the application requirements of marine engineering. After years of efforts by professionals in the titanium industry and researchers in marine engineering applications, titanium has been widely used in fields such as offshore oil and gas development, port construction, coastal power plants, seawater desalination, shipbuilding, marine fisheries, and ocean thermal energy conversion. Nowadays, titanium used in marine engineering has become one of the main fields for civilian applications of titanium.
-
-
-
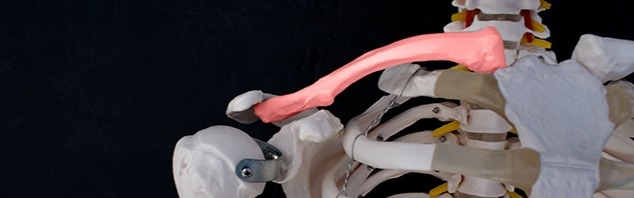
Artificial joint
-
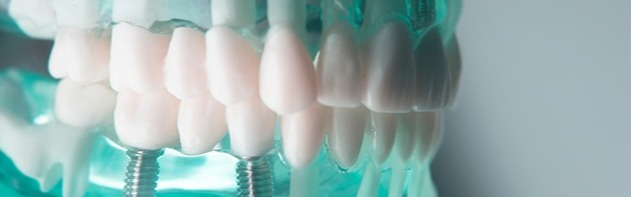
Artificial dental implants and orthodontic treatment
-
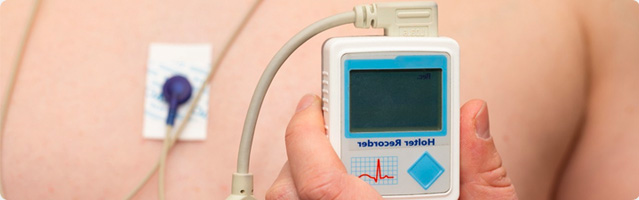
Pacemaker
Biomedicine
Titanium has similar properties to human bones and has good biocompatibility and no toxic side effects on human tissues. Human implants are special functional materials closely related to human life and health.
Compared with other metal materials, the advantages of using titanium and titanium alloys mainly include the following: lightweight, low elastic modulus, no impact, nontoxicity, corrosion resistance, high strength, and good toughness.
The amount of titanium alloy used in surgical implants is increasing at a rate of 5%-7% per year.
-
-
-

Sports Equipment
Golf head, tennis racket, badminton racket, billiards club, hiking stick, ski stick, ice skate
-

Articles for Daily Use
Glasses frames, watches, canes, fishing rods, kitchenware, digital product casings, handicrafts, decorations
Daily Life
Titanium, with its lightweight and high-strength characteristics, has gradually expanded its application in sports equipment from tennis rackets and badminton rackets to golf heads, clubs, and racing cars. In 2008, sports and leisure accounted for 13% of total consumption in China, with over 1000 tons of titanium used for golf heads and clubs alone. Bicycle frames made of titanium alloy are also popular. The United States has long been the largest producer and consumer of titanium bicycles. The lightweight characteristics of titanium have also been applied to eyeglass frames, with the additional benefit of being hypoallergenic to the skin. Moreover, the surface of titanium can have brilliant colors after anodizing, so it has been used in eyeglass frames since the early 1980s.
-
-
-

Petrochemical Industry
-

Chlor-alkali
-

Soda ash
-

Plastics
Metallurgical and Chemical Industry
Compared with traditional metal alloys such as stainless steel and nickel, titanium, zirconium, and their alloys have excellent corrosion resistance and can resist the corrosion damage of most organic acids, inorganic acids, strong bases, and certain molten salts. In wastewater treatment, food processing, and strong acid production industries, they are mainly used in equipment and components requiring high corrosion resistance, such as reaction vessels, acid-proof pumps, heat-resistant pumps, heat exchange tubes, immersion devices, acid-proof impellers, valves, stirrers, nozzles, and linings of electric appliances. The equipment and devices with these materials used by American chemical companies have operated for over 25 years and have not been significantly affected by corrosion, resulting in a conversion rate as high as 85%-90%, which greatly improves the production efficiency of the companies. In the process of deep-sea exploration, titanium and zirconium alloys can not only withstand the erosion, corrosion, and friction wear of seawater and sand in the ocean, but also adapt to alternating temperature environments of -200 to 200℃. This is because titanium and zirconium have low thermal expansion coefficients and can be stably and continuously used.
-
-
-

Automobile connecting rod
-

High-performance automotive valves
-

Dual exhaust system
Automobile Industry
Lightweight automobiles are an effective measure to save fuel and reduce pollution. For every 10% decrease in the weight of a car, fuel consumption can be saved by 8%-10%, and exhaust emissions can be reduced by 10%.
In terms of driving, the acceleration performance of cars has been improved after lightweighting, and there have also been improvements in vehicle control stability, noise, and vibration. From the perspective of collision safety, after lightweighting, cars have less inertia and reduced braking distance during collisions. In 2009, the global amount of titanium used in automobiles reached 3,000 tons. Titanium has been used in racing cars for many years. Currently, almost all racing cars use titanium materials. The amount of titanium used in Japanese cars has exceeded 600 tons. With the development of the global automotive industry, the use of titanium in cars is rapidly increasing.
-
Synthetic Rutile
Zircon sand
Rutile
Reduced ilmenite
Iron oxide red
Coal-based activated carbon
Application Areas


